How does an SSL certificate work?
How does an SSL certificate work?
An SSL certificate ensures safe, easy, and convenient Internet shopping. Once an Internet user enters a secure area — by entering credit card information, email address, or other personal data, for example — the shopping site’s SSL certificate enables the browser and Web server to build a secure, encrypted connection. The SSL “handshake” process, which establishes the secure session, takes place discreetly behind the scene without interrupting the consumer’s shopping experience. A “padlock” icon in the browser’s status bar and the “https://” prefix in the URL are the only visible indications of a secure session in progress.
By contrast, if a user attempts to submit personal information to an unsecured website (i.e., a site that is not protected with a valid SSL certificate), the browser’s built-in security mechanism triggers a warning to the user, reminding him/her that the site is not secure and that sensitive data might be intercepted by third parties. Faced with such a warning, most Internet users will likely look elsewhere to make a purchase.
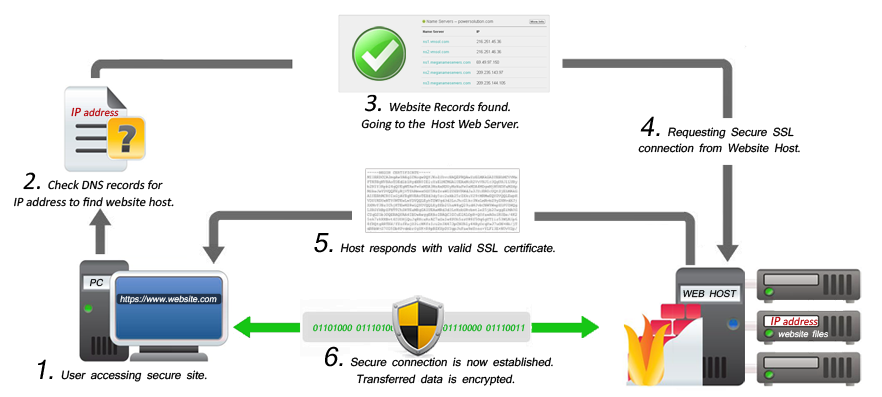
What Happens When a Visitor Opens a Website with SSL Certificate Security in his Browser.
- User tries to visit the SSL secured website with his browser.
- The browser/ISP query the DNS servers to identify the web hosting server.
- The web server sends a SSL certificate and requests a secure connection.
- User’s Browser verifies the authenticity of the SSL Certificate and if it’s valid then agrees for a secure connection.
- Web server accepts confirmation and transmits digital signatures to initiate a SSL secured connection with browser.
- Data transfer is encrypted between the browser and server and adds HTTPS in the URL.
Strong encryption ensures that no one else could read or decode the data that’s being shared between server and user system. SSL certificate protects the data transfer by creating secure channel between web hosting server and user’s browser. SSL Certificate performs a handshake with user’s computer’s browser and sends a public key to the browser so that browser can confirm the recognition and validate the trust. Once the trusted connection is established, data transfer begins.
Iwebslog powered 256 bit strong encryption will take trillion of years for a hacker to break it with all the latest software, hardware tools and time. Therefore, technically we consider it as unbreakable by the method of brute force. Ideally a website should use an encryption of at-least 128 bits a security protocol being adopted by most of the banks across the globe. We keep your website above these standards by providing you with the 256 bits encryption.
Credentials required to Verify The Identity Online
We as a Certifying Authority may require several credentials or documents to validate your domain, personal or your company’s identity. These may include – driver’s license, a passport, a company ID Card, National Citizenship Proof or a Voter ID or Bills relating to your House or Business Location or Bank/credit card statements. SSL Certificates are unique and issued based on these documents to a specific individual or a domain or a company/business. You can review the validation and verify the trustworthiness by clicking on padlock in the address bar of browser/Security Seal at the bottom/Trust mark on the payment gateway pages. You can check it by clicking on this padlock icon and see the certificate.